Understanding and reporting carbon emissions can help identify ways of improving environmental performance and cutting costs. The carbon reporting practice is underpinned by the use of internationally recognized standards like the Greenhouse Gas Protocol and the ISO 14064-1 standard. Carbon footprint accounting is based on five principles, which include:
Relevance. Ensure that the carbon footprint report to a company reflects the greenhouse gas emissions attributed to the organization.
Completeness. Accounting and reporting all greenhouse gas emissions sources within the defined boundary of the organization.
Consistency. The use of consistent methodologies allow for meaningful comparisons of carbon emission reports over time.
Transparency. Information should be complied, analyzed and documented clearly, so auditors may evaluate its credibility at a later point.
Accuracy. Ensuring uncertainties in data are reduced as far as practicable and when the uncertainty is high use conservative factors. This is important to enable users to make decisions with reasonable assurance as to the integrity of the reported information.
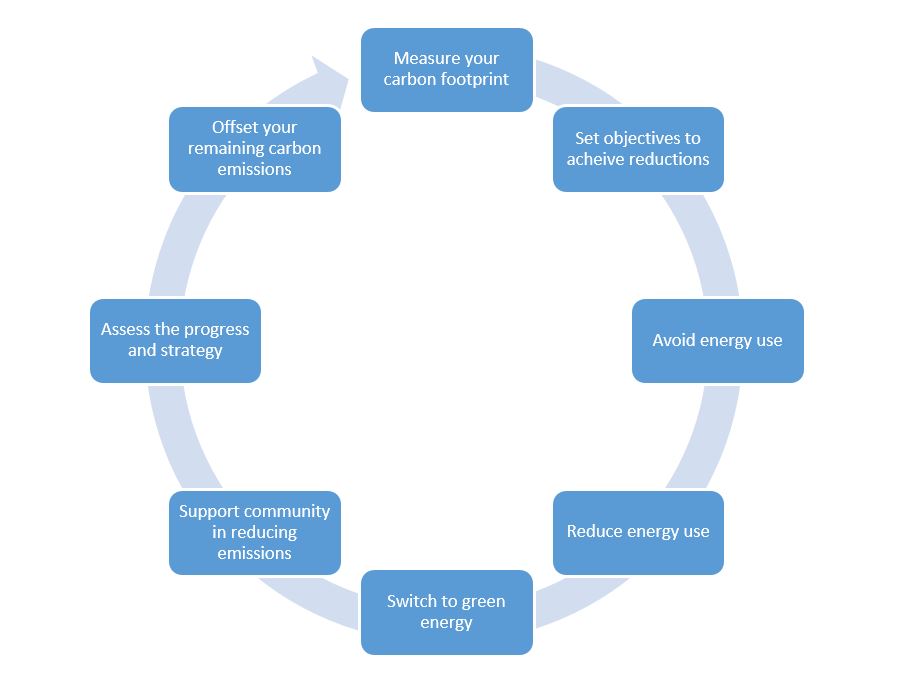
Web based tools produced by governments contains emission conversion factors for greenhouse gas reporting. These factors help businesses to convert their internal and external activities into the equivalent carbon emissions. The following carbon management principles are considered best practice.