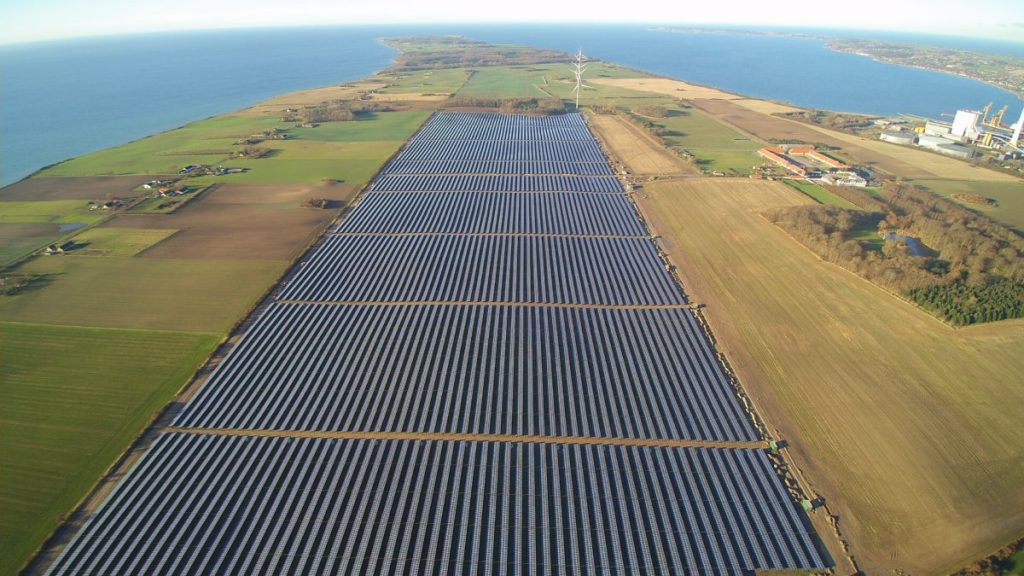
Continental's Renewable Electricity Portfolio by Technology
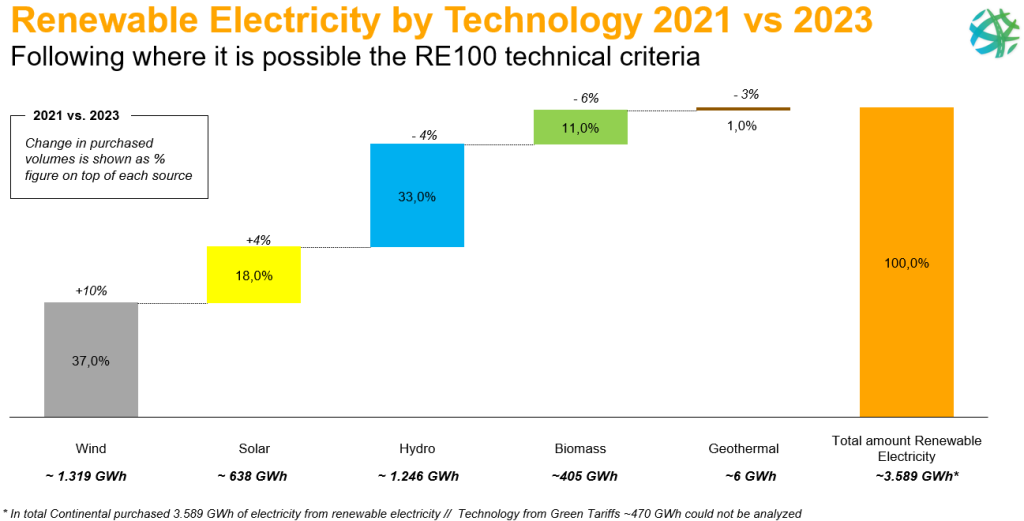
Continental do take care about the renewable electricity technology used and is following the guidance wherever it is possible from the technical criteria of the RE100.
Inside Continental's Holistic Renewable Electricity Portfolio
The holistic renewable electricity portfolio of Continental contains a mix of Power Purchase Agreements, Long term EAC contracts, classical EAC contracts, Green Tariffs and Self Generation.
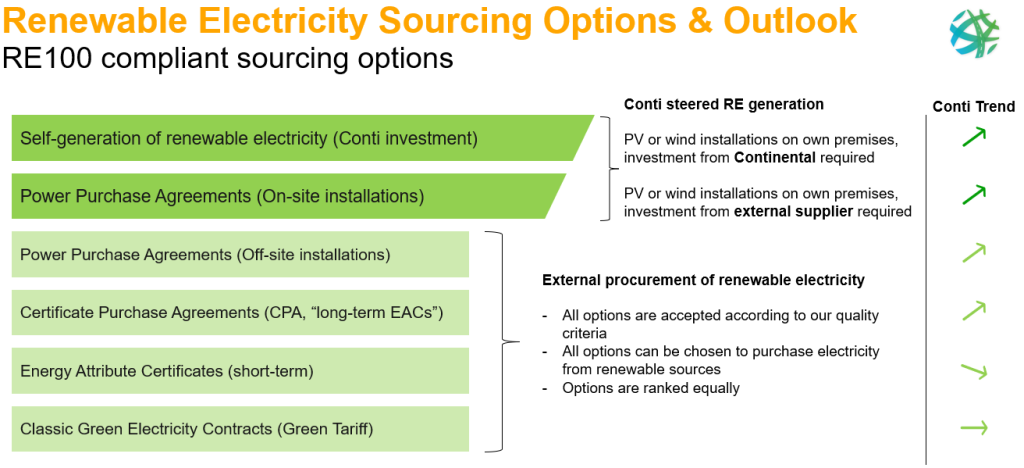
We project a strong growth of on site self generated renewable electricity.
Our Continental-Industria Textil do Ave site in Portugal is a great example:


The production of renewable electricity is certified by Energy Attribute Certificates (EACs). These are the accepted legal instrument through which claims of renewable energy generation and consumption are substantiated in the global renewable energy market. There are different types of EAC for different regions of the world, and they are all in compliance with the quality criteria set by the Greenhouse Gas Protocol in the latest Scope 2 guidance document.


















